What is Margin in Forex Trading?
Margin refers to the amount of money that a trader needs to hold in their trading account to open and maintain a leveraged position in the forex market. It is the collateral required by the broker to cover any potential losses that may occur on the trader's position. Margin is usually expressed as a percentage of the full value of the position, known as the margin requirement.
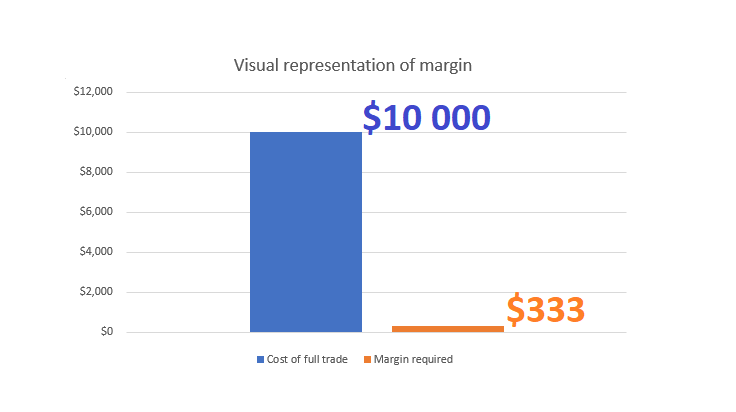
Example to Understand Margin:
Suppose a trader wants to open a position in the EUR/USD currency pair with a notional value of $100,000 and a leverage of 100:1. This means that the trader needs to hold a margin of 1% of the position size in their account, which is $1,000. The remaining $99,000 will be provided by the broker as a loan. If the value of the position drops by 1%, the trader's equity will be wiped out, and the position will be closed automatically by the broker to prevent further losses.
Margin requirements vary depending on the broker and the currency pair being traded. Higher margin requirements are usually applied to more volatile currency pairs or during times of high market volatility to mitigate the risk of large losses.